
- +91 8055996347
- info@3dreality.in
- Chapru nagar square, CA road, Nagpur, Maharashtra-440008
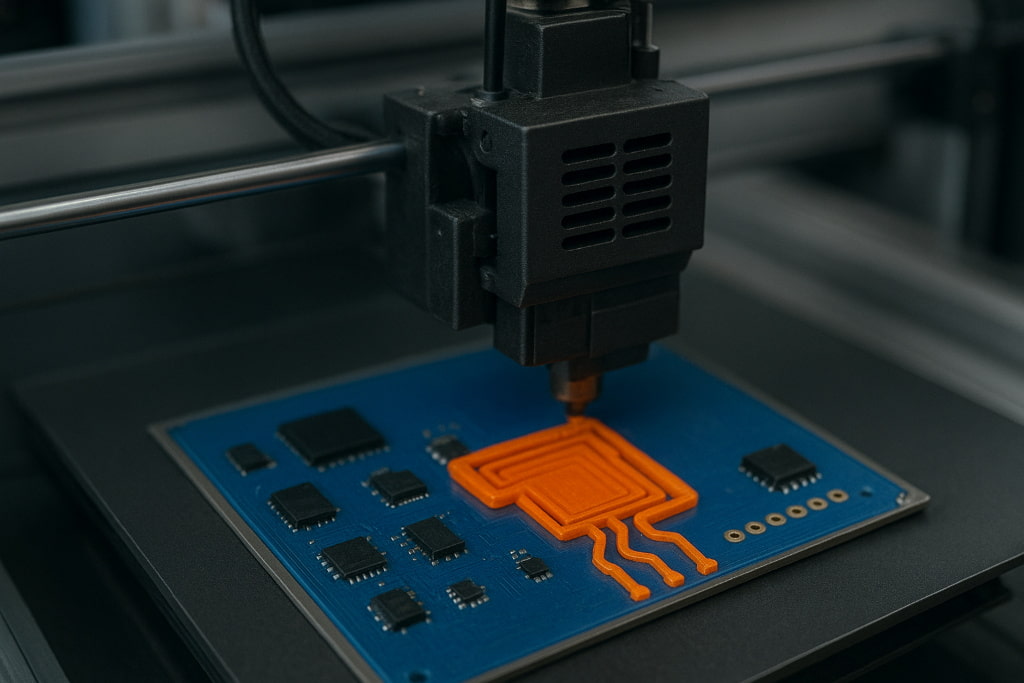
3D printing has already transformed industries like healthcare, aerospace, and automotive. But one of the most exciting frontiers today is 3D printing in electronics. From flexible circuits to smart wearables, this technology is opening the door to faster innovation, lower costs, and highly customized designs. As the electronics industry continues to grow, 3D printing is expected to play a central role in shaping its future.
In this blog, we’ll explore the opportunities and challenges of 3D printing in electronics, explained in simple terms so everyone can understand.
3D printing in electronics involves creating electronic components like circuit boards, sensors, and connectors layer by layer, using specialized materials such as conductive inks or polymers. Instead of relying on traditional methods that require complex assembly lines, 3D printing allows designers and engineers to produce electronic parts directly from digital designs.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is speed. In traditional manufacturing, designing and testing a new electronic device can take weeks or months. With 3D printing, prototypes can be made in just a few hours. This allows companies to test new designs quickly, make changes, and bring products to market faster.
Electronics manufacturing often requires expensive tools, molds, and labor. 3D printing eliminates many of these steps, significantly reducing costs. This is especially useful for startups and small businesses that want to test new ideas without heavy investment.
Imagine custom-made circuit boards designed specifically for your device. With 3D printing, electronics can be easily personalized to fit different shapes, sizes, or functions. This flexibility is vital in industries like wearables, IoT devices, and medical electronics where every product may need unique features.
3D printing enables the integration of multiple components into a single structure, reducing the number of parts needed. This leads to smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices—a huge advantage for mobile gadgets, drones, and medical implants.
Traditional electronics production creates a lot of waste. 3D printing uses only the exact material required, making it more eco-friendly. By reducing waste and energy consumption, it supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
Currently, there are only a few materials available that can conduct electricity effectively and be used in 3D printers. This limits the complexity of devices that can be manufactured compared to traditional methods.
While 3D printing is great for prototyping and small batches, it still struggles with mass production. Printing large quantities of electronics can be time-consuming, which may slow down adoption in big industries.
Electronics created with 3D printing may not always match the strength and reliability of those produced with conventional methods. This is especially critical for devices used in aerospace, automotive, or medical fields where safety is essential.
Although 3D printing reduces costs in the long run, the initial investment in advanced printers and materials can be high. This makes it difficult for some companies to adopt the technology immediately.
The electronics industry depends on strict quality standards. Since 3D printing in electronics is still developing, there aren’t many established standards, which can cause challenges in quality control and large-scale adoption.
Despite these challenges, the future of 3D printing in electronics is bright and promising. As research continues, new materials will be developed, printers will become faster, and devices will be more reliable. Over time, this technology could completely transform the way we design and manufacture electronics, from smartphones to smart homes.
In fact, experts believe that in the next decade, we may see fully 3D-printed electronic devices that are lighter, cheaper, and more advanced than anything available today.
3D printing in electronics offers enormous opportunities—speed, customization, cost savings, and sustainability—while also facing challenges like limited materials, slower mass production, and quality concerns. But as technology evolves, these barriers will be reduced, paving the way for a new era of innovation in electronics manufacturing.
At 3DReality, we provide professional 3D printing services tailored to your needs. Whether you need custom prototypes, product designs, or innovative electronic components, our team is here to help bring your ideas to life. We specialize in designing all types of products with precision and creativity.